Open Question
Open Question
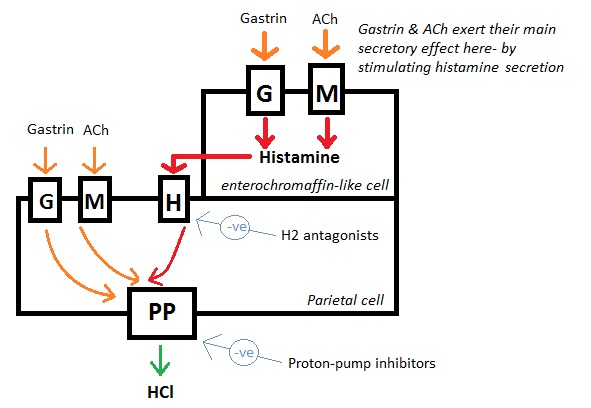
The parietal cell secretes HCl. This is regulated by gastrin, histamine and muscarinic receptors.
If you blocked any one of them, this would result in reduced HCl. However, this effect is particularly prominent with antihistamine blockade.
This is because although gastrin and acetylcholine exert their effects on the gastrin and muscarinic receptors on the parietal cells, their main effect is on enterochromaffin-like cells. These are the cells which release histamine. So in effect, the main effect of gastrin and acetylcholine is release of histamine, not direct stimulation of HCl secretion. Therefore the most effective receptor to block, would be the histamine receptors!
This is how drugs like ranitidine, cimetidine, famotidine, and nizatadine work.
Diagram adapted from Fig 10.2. Dawson, Taylor, Reide. Pharmacology. Crash Course 2nd Edition, Mosby.